FP7 is the short name for the Seventh Framework Programme for Research and Technological Development. This was the EU's main instrument for funding research in Europe, running from 2007 to 2013. FP7 was designed to respond to Europe's employment needs, competitiveness, and quality of life.
The Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) classification system, divides active substances into different groups according to the organ or system on which they act and their therapeutic, pharmacological and chemical properties. Drugs are classified in groups at five different levels, Drugs are divided into fourteen main groups (1st level), with pharmacological/therapeutic subgroups (2nd level). The 3rd and 4th levels are chemical/pharmacological/therapeutic subgroups and the 5th level is the chemical substance. The Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) classification system and the Defined Daily Dose (DDD) is a tool for exchanging and comparing data on drug use at international, national or local levels.
The Antibody Registry provides identifiers for antibodies used in publications. It lists commercial antibodies from numerous vendors, each assigned with a unique identifier. Unlisted antibodies can be submitted by providing the catalog number and vendor information.
The BRCA Exchange website is a product of the BRCA Challenge of the Global Alliance for Genomics and Health. It provides information on catalogued BRCA1 and BRCA2 genetic variants. By default, it shows variants that have been curated and classified by an international expert panel, the ENIGMA consortium, to assess their pathogenicity (associated disease risk). Optional settings allow the user to look at unclassified variants.
The cellosaurus is a knowledge resource on cell lines. It attempts to describe all cell lines used in biomedical research. Bairoch A. The Cellosaurus, a cell line knowledge resource. J. Biomol. Tech. (2018) 29:25-38 DOI: 10.7171/jbt.18-2902-002, PMID: 2980532
Chemical Entities of Biological Interest (ChEBI) is a freely available dictionary of molecular entities focused on 'small' chemical compounds.
ChEMBL is a database of bioactive drug-like small molecules, it contains 2-D structures, calculated properties (e.g. logP, Molecular Weight, Lipinski Parameters, etc.), and abstracted bioactivities (e.g. binding constants, pharmacology, and ADMET data). The data is abstracted and curated from the primary scientific literature, and cover a significant fraction of the SAR and discovery of modern drugs.
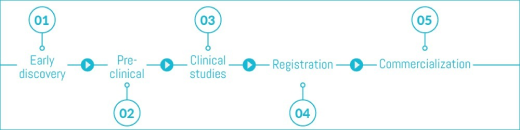
ClinicalTrials.gov provides free access to information on clinical studies for a wide range of diseases and conditions. Studies listed in the database are conducted in 175 countries
ClinVar archives reports of relationships among medically important variants and phenotypes. It records human variation, interpretations of the relationship-specific variations to human health, and supporting evidence for each interpretation. Each ClinVar record (RCV identifier) represents an aggregated view of interpretations of the same variation and condition from one or more submitters. Submissions for individual variation/phenotype combinations (SCV identifier) are also collected and made available separately. This collection references the Record Report, based on RCV accession.
The Cooperative Patent Classification (CPC) is a patent classification system, developed jointly by the European Patent Office (EPO) and the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO). It is based on the previous European classification system (ECLA), which itself was a version of the International Patent Classification (IPC) system. The CPC patent classification system has been used by EPO and USPTO since 1st January 2013.
The Community Research and Development Information Service (CORDIS) is the European Commission's primary source of results from the projects funded by the EU's framework programmes for research and innovation (FP1 to Horizon 2020).
DailyMed provides information about marketed drugs. This information includes FDA labels (package inserts). The Web site provides a standard, comprehensive, up-to-date, look-up and downloads resource of medication content and labeling as found in medication package inserts. Drug labeling is the most recently submitted to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and is currently, in use, it may include, for example, strengthened warnings undergoing FDA review or minor editorial changes. These labels have been reformatted to make them easier to read.
The dbSNP database is a repository for single base nucleotide substitutions, short deletion, and insertion polymorphisms. The dataset loaded in DISQOVER includes all variants with a cross-reference from SwissVar, DisGeNET, and Provean. In addition, it covers all variants of a manually curated subset of genes that are somatically mutated and causally implicated in human cancer from the COSMIC database.
dbVar is NCBI's database of genomic structural variation. It houses variation data generated mostly by published studies of various organisms. Variants typically have lengths of 50 nucleotides or longer.
DrugCentral provides information on active ingredients chemical entities, pharmaceutical products, drug mode of action, indications, and pharmacologic action.

.png)